本日の目標
- 対象とするデータを構造体として表現することができる。
- 構造体を使った簡単なプログラムをつくることができる。
予習・復習
以下のスライドを利用して、予習と復習をしよう。復習では、自分の理解度を確認するために、実際にプログラムを作成し、意図する結果が得られるか確認しよう。本日の講義・演習予定
- 構造体
- 構造体を配列で利用する
- 構造体の中の構造体
- 構造体を戻り値とする関数
- 共用体
- 列挙体
- 演習問題
- 提出課題
struct 構造体タグ名
{
メンバ名1;
メンバ名2;
・・・
};
struct point {
int x;
int y;
};
struct 構造体タグ名 オブジェクト名 [, オブジェクト名, ・・・];
struct point p;
#include <stdio.h>
struct point{
int x;
int y;
};
int main(void)
{
struct point p;
p.x = 5;
p.y = 8;
printf("座標(%d,%d)\n", p.x, p.y);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
struct point{
int x;
int y;
};
int main(void)
{
struct point p = {5, 8}; //構造体変数の初期化
printf("座標(%d,%d)\n", p.x, p.y);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
struct point{
int x;
int y;
};
int main(void)
{
struct point a = {2,3}, b = {4,5};
a.x += b.x;
a.y += b.y;
// a += b; とはできない!
printf("(%d, %d)\n", a.x, a.y);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
struct point{
int x;
int y;
};
int main(void)
{
struct point a,b;
printf("座標A(x,y)> ");
scanf("%d,%d", &a.x, &a.y);
b = a; //構造体のコピー
printf("座標a(%d,%d)\n", a.x, a.y);
printf("座標b(%d,%d)\n", b.x, b.y);
return 0;
}
・・
struct point {
int x;
int y;
};
typedef struct point Point;
int main(void)
{
Point point;
・・・
typedef struct point {
int x;
int y;
} Point;
typedef struct Point {
int x;
int y;
} Point;
typedef struct {
int x;
int y;
} Point;
typedef struct {
int x;
int y;
} Point, Vector;
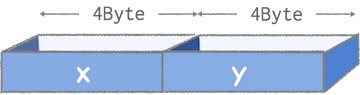
struct song{
char name[128]; //曲名
int time; //演奏時間(秒)
double size; //データサイズ(MB)
}
となります。タイトルには文字列を格納するためにchar型配列を、演奏時間にはint型を、データサイズには小数点を含む数を扱えるようにdouble型としました。ある楽曲Aを構造体songを使って表せば、「Aの曲名」、「Aの演奏時間」、「Aのデータサイズ」のようにAという名前でひとくくりにして管理することができるようになります。(文字列の扱い方についてはプログラミング4で詳しく学びます。)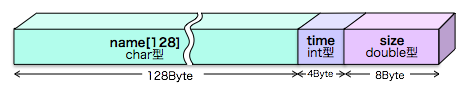
#include <stdio.h>
struct song{
char name[128];
int time;
double size;
};
typedef struct song Song;
int main(void)
{
Song sakura= {"SAKURA", 281, 12.5};
printf("曲名: %s 演奏時間: %d(sec) サイズ:%.2f(MB) ¥n", sakura.name, sakura.time, sakura.size);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 4
typedef struct point{
int x,y;
} Point;
int main(void)
{
Point p[N] = {{0,0}, {0,5}, {5,5}, {5,0}} //構造体変数の初期化
int i;
for(i=0; i<N; i++)
printf("座標%d(%d, %d)¥n", i, p[i].x, p[i].y);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 4
typedef struct point{
int x, y;
} Point;
int main(void)
{
Point p[N];
int i;
for(i=0; i<N; i++){
printf("座標%d/n",i+1);
printf("x>> "); scanf("%d", &p[i].x);
printf("y>> "); scanf("%d", &p[i].y);
}
for(i=0; i<N; i++)
printf("座標%d(%d, %d)¥n", i, p[i].x, p[i].y);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct {
int x, y;
} Point;
struct line{
int id; //ID
Point start; //始点
Point end; //終点
char attribute; //属性
};
typedef struct line Line;
int main(void)
{
Point a = {0,0};
Point b = {200,350};
Line line = {1000,a,b,0xff};
printf("ID : %d\n",line.id);
printf("始点: (%d,%d)\n", line.start.x, line.start.y);
printf("終点: (%d,%d)\n", line.end.x, line.end.y);
printf("属性: 0x%02x\n", line.attribute);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
struct line{
int id;
struct point {
int x;
int y;
} start,end; //始点,終点
char attribute; //属性
};
typedef struct line Line;
int main(void)
{
Line line = {1000,0,0,100,200,0xff};
printf("id : %d\n",way.id);
printf("始点: (%d,%d)\n",line.start.x,line.start.y);
printf("終点: (%d,%d)\n",line.end.x,line.end.y);
printf("属性: 0x%02x\n",line.attribute);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct vector {
int x,y;
} Vector;
Vector add(Vector a, Vector b)
{
Vector v;
v.x = a.x + b.x;
v.y = a.y + b.y;
return v;
}
int main(void)
{
Vector p1 = {7,5};
Vector p2 = {10,20};
Vector p3;
p3 = add(p1, p2);
printf("合成ベクトル( %d, %d)\n", p3.x, p3.y);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 3
typedef struct vector {
int x,y;
} Vector;
Vector sumOf(Vector a[])
{
Vector s = {0,0};
int i;
for(i=0; i<N; i++){
s.x += a[i].x;
s.y += a[i].y;
}
return s;
}
int main(void)
{
Vector v[N] = {{3,-1},{2,6},{-3,2}};
Vector d;
d = sumOf(v);
printf("(%d,%d)\n", d.x, d.y);
return 0;
}
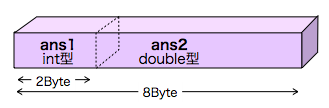
#include <stdio.h>
union answer{
int seki; //積
double syo; //商
};
int main(void)
{
int a,b;
union answer ans;
printf("積と商を求めます。2つの整数を入力してください。¥n");
printf(">> ");
scanf("%d,%d", a,b);
ans.seki=a*b;
printf("積:%d¥n",ans.seki);
ans.syo=a/b;
printf("商:%f¥n",ans.syo);
return 0;
}
enum タグ名{
定数名, // 0
定数名, // 1
定数名, // 2
・・・
}
#include <stdio.h>
enum Number{
Zero,
One,
Two
};
int main(void)
{
enum Number num;
num = One;
printf("%d\n",num);
return 0;
}
enum Number{
Zero,
One,
Two,
Ten = 10,
Eleven
};
struct division{
int syo; //商
int amari; //剰余
}
struct mystack {
int top;
int data[STACKSIZE];
}
今週の確認テスト テスト(PDF)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define Nenpi 10.0 // 燃費[km/L]
typedef struct {
double x,y; //位置の座標
} Position;
typedef struct {
Position p; // 位置
double fuel; // 燃料の残量
} Car;
/* 移動距離 */
double distance(Car car1, Car car2)
{
//ここを埋めて完成させる
}
int main(void)
{
Car rescue = {{0,0},50}; //救援車 <-訂正(再提出不要)
Car car; //救援対象車
double d; //距離
double remain; //残燃料
car.fuel = 0.; //燃料が0に
printf("救援を求めている車の現在位置(x,y)> ");
scanf("%lf,%lf",&car.p.x, &car.p.y);
d = distance(car, rescue); //移動距離
remain = [空欄ア]; //ここを埋めて完成させる。救援車の残燃料
if(remain > 25)
printf("往復分の燃料があります。(残燃料: %f リットル)\n",remain);
else if (remain> 0)
printf("往復分の燃料はありません。(残燃料: %f リットル)\n",remain);
else
printf("燃料が足りません。\n");
return 0;
}