本日の目標
- 動的にメモリを管理する仕組みを知る。
- mallocを使って、必要に応じた分だけメモリ領域を確保し利用するプログラムが書ける。
予習・復習
以下のスライドを利用して、予習と復習をしよう。復習では、自分の理解度を確認するために、実際にプログラムを作成し、意図する結果が得られるか確認しよう。本日の講義・演習予定
- 動的メモリ管理
- 構造体と動的メモリ管理
- 演習
- 演習問題
- 提出課題
| 関 数 | 説 明 |
|---|---|
| void *malloc(size_t size) | sizeバイト分のメモリ領域を確保する。 [戻り値]成功:確保した領域の先頭を指すポインタ 失敗:NULL |
| void* calloc(size_t n, size_t n) | sizeバイト分のメモリ領域を確保する。 [戻り値]成功:確保した領域の先頭を指すポインタ 失敗:NULL |
| void* reallooc(void *ptr, size_t size) | ptrで示すメモリ領域のサイズをsizeバイトに変更する [戻り値]成功:確保した領域の先頭を指すポインタ 失敗: |
| void free(void *ptr) | ptrで示すメモリ領域を解放する。 |
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 5
int main(void)
{
int score[N];
int i,max=0,sum=0;
for(i=0; i<N; i++){
printf("%d人目の点数>> ",i+1);
scanf("%d",&score[i]);
}
for(i=0; i<N; i++){
sum += score[i];
if(score[i] > max) max = score[i];
}
printf("平均点 %.1f\n",(double)sum/N);
printf("最高点 %d\n",max);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
int *p;
int i,max=0,sum=0;
int num;
printf("何人分の点数ですか?> ");
scanf("%d",&num);
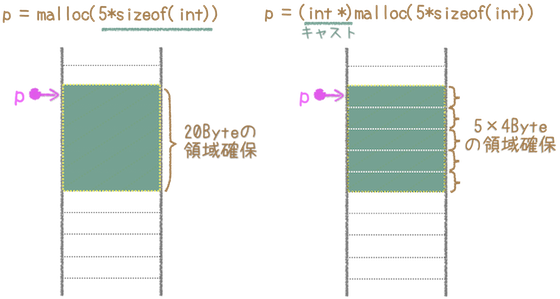
p = (int *)malloc(num*sizeof(int)); //領域確保
if(p==NULL){ //領域確保に失敗した場合
fprintf(stderr,"Error: Malloc failed");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
for(i=0; i<num; i++){
printf("%d人目の点数>> ",i+1);
scanf("%d",p+i);
}
for(i=0; i<num; i++){
sum += *(p+i);
if(*(p+i) > max) max = *(p+i);
}
printf("平均点 %.1f\n",(double)sum/num);
printf("最高点 %d\n",max);
free(p); //領域解放
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
char *p1,*p2;
p1 = (char *)malloc(100*sizeof(char)); //領域確保
if(p1==NULL){ //領域確保に失敗
fprintf(stderr,"Error: P1 Malloc failed");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
p2 = (char *)realloc(p1,200*sizeof(char)); //2倍に拡張
if(p2==NULL){ //領域確保に失敗
fprintf(stderr,"Error: P2 Malloc failed");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
p1 = p2; //ポインタp1で指し示す
free(p1); //p1とp2は同じ領域を示しているので
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
int *p1,*p2,*p3;
int i,max=0,sum=0;
int num=5;
p1 = (int *)malloc(500*sizeof(int)); //領域確保
if(p1==NULL){ //領域確保に失敗
fprintf(stderr,"Error: P1 Malloc failed");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
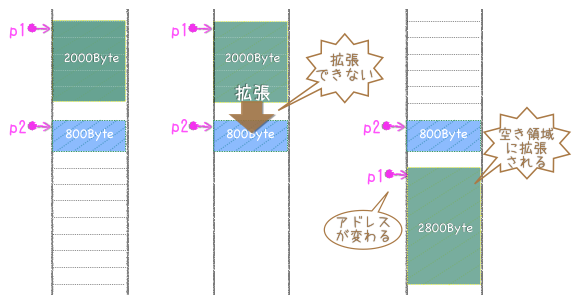
printf("メモリブロックp1 (%p)\n",p1);
p2 = (int *)malloc(200*sizeof(int)); //領域確保
if(p2==NULL){ //領域確保に失敗
fprintf(stderr,"Error: P2 Malloc failed");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
printf("メモリブロックp2 (%p)\n",p2);
p3 = (int *)realloc(p1,700*sizeof(int)); //領域確保
if(p3==NULL){ //領域確保に失敗
fprintf(stderr,"Error: P3 Malloc failed");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
p1 = p3;
printf("拡張したメモリブロックp1 (%p)\n",p1);
free(p1);
free(p2);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct student{
int id;
char name[32];
};
typedef struct student Student;
int main(void)
{
Student *sp;
int num,i;
printf("学生数> ");
scanf("%d",&num);
if((sp=(Student *)malloc(sizeof(Student)*num))==NULL){
fprintf(stderr,"Error: Memory allocation failure.\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
for(i=0; i<num; i++){
(sp+i)->id = 1000+i;
printf("名前> ");
scanf("%s",(sp+i)->name);
}
for(i=0; i<num; i++)
printf("%d: %s\n",(sp+i)->id,(sp+i)->name);
free(sp);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 座標
struct point2d {
int x;
int y;
};
typedef struct point2d Point;
int main(void)
{
Point *p;
int i,n,sum=0;
printf("多角形の頂点数> ");
scanf("%d", &n);
p = [[空欄ア]]; //領域確保
printf("反時計回りに座標を入力してください。\n");
for(i=0; i<n; i++){
printf("座標%d(x,y)> ",i);
scanf("%d,%d", [[空欄イ]], [[空欄ウ]]);
}
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++){
sum += (p+i)->x * (p+i+1)->y - [[空欄エ]] *[[空欄オ]];
}
sum += (p+n-1)->x * p->y - (p+n-1)->y * p->x; //最初の座標と
printf("面積: %f\n",(float)sum/2);
[[空欄カ]]; //領域解放
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <tstdlib.h>
// 座標
struct point2d {
int x;
int y;
};
typedef struct point2d Point;
//平面図形
struct polygon{
int nvertices; //頂点数
Point *p; //各頂点の座標
};
typedef struct polygon Shape;
int main(void)
{
Shape shape;
int i,n,sum=0;
printf("多角形の頂点数> ");
scanf("%d", &n);
[[空欄ア]] = (Point *)malloc(sizeof(Point)*n); //領域確保
printf("反時計回りに座標を入力してください。\n");
for(i=0; i<n; i++){
printf("座標%d(x,y)> ",i+1);
scanf("%d,%d",[[空欄イ]], [[空欄ウ]]);
}
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++){
sum += (shape.p+i)->x * (shape.p+i+1)->y - [[空欄エ]] * [[空欄オ]];
}
sum += (shape.p+n-1)->x * shape.p->y - (shape.p+n-1)->y * shape.p->x;
printf("面積: %f\n",(float)sum/2);
[[空欄カ]];
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//座標
struct point2d {
int x;
int y;
};
typedef struct point2d Point;
//平面図形
struct polygon {
int id;
int nvertices; //頂点数
Point *p; //各頂点の座標
};
typedef struct polygon Shape;
int main(void)
{
Shape shape;
int i,n;
do{
printf("頂点数> ");
scanf("%d",&n);
}while(n<1);
shape.nvertices = n;
shape.p = [[空欄ア]] ; //領域確保
shape.id = 1001;
for(i=0; i<n; i++){
printf("頂点%dの座標(x,y) > ",i+1);
scanf("%d,%d", [[空欄イ]]->x, [[空欄イ]]->y);
}
switch(shape.nvertices){
case 1: printf("点"); break;
case 2: printf("直線"); break;
default: printf("%d角形",n); break;
}
printf("(%d): ",shape.id);
for(i=0; i<n; i++){
printf("(%d,%d) ", [[空欄ウ]]->x, [[空欄ウ]]->y); //頂点座標
}
printf("\n");
[[空欄エ]];
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//座標
struct point2d {
int x;
int y;
};
typedef struct point2d Point;
//平面図形
struct polygon {
int id;
int nvertices; //頂点数
Point *p; //各頂点の座標
};
typedef struct polygon Shape;
int main(void)
{
Shape *ps; //図形群へのポインタ
int i,j,ns,np; //図形数、頂点数
printf("図形の数> ");
scanf("%d",&ns);
ps = [[空欄ア]]; //領域確保
for(i=0; i<ns; i++){
(ps+i)->id = 1001+i;
printf("\nID:%d ----------\n", (ps+i)->id);
printf("何角形> ");
scanf("%d",&np);
(ps+i)->nvertices = np;
[[空欄イ]] = (Point *)malloc(sizeof(Point)*np); //領域確保
for(j=0; j<np; j++){
printf("座標%d(x,y) > ",j+1);
scanf("%d,%d", [[空欄ウ]]->x, [[空欄ウ]]->y);
}
}
for(i=0; i<ns; i++){
printf("%d: ",(ps+i)->id);
switch((ps+i)->nvertices){
case 1: printf("点"); break;
case 2: printf("直線"); break;
default: printf("%d角形 ",(ps+i)->nvertices); break;
}
for(j=0; j<(ps+i)->nvertices; j++)
printf("(%d,%d) ", [[空欄エ]]->x, [[空欄エ]]->y); //頂点座標
printf("\n");
[[空欄オ]]; //各頂点のための領域解放
}
[[空欄カ]]; //図形のための領域解放
return 0;
}
1月> January 2月> February ・・・
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define N 12 //12ヶ月
int str_len(char s[])
{
int len=0;
for(len=0; s[len]!='\0'; len++);
return len;
}
int main(void)
{
char *p[N] = {NULL}; //N個のポインタからなる配列
char str[16];
int len,i,j;
printf("月名の英単語を入力してください\n");
for(i=0; i<N; i++){
printf("%d月> ",i+1);
scanf("%s",str);
len = str_len(str); //文字数
p[i] = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*(len+1)); //文字数分の領域確保,NULL文字分を加える
if(p[i] == NULL){
fprintf(stderr,"Error: Memory allocation failure.\n");
for(j=0; j<i; j++) free(p[j]); //確保済領域の解放
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
for(j=0; j<=len; j++) p[i][j] = str[j];
getchar(); //改行文字の読み込み
}
for(i=0; i<N; i++) printf("%s\n",p[i]); //結果表示
for(i=0; i<N; i++) free(p[i]); //12個の領域を解法
return 0;
}
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define NUM 10 //冊数
/* 書名データ */
const char data[][32] = {
"Al8gorithms",
"Artif1icial Intel99ligence",
"Autom3ata",
"Co7mput6er Architecture",
"Deep Learning8",
"Desi4gn 7Patterns",
"M3achine Learning",
"1Numerical 1Analysis",
"Object Orie65nted design",
"Programm3ing Langu98ages"};
/* 文字列から数字を取って、文字数を返す */
int scrape(char dst[], const char src[])
{
int i,len=0;
for(i=0; src[i]!='\0'; i++){
if([空欄]) continue; //数字ならば以下の処理を飛ばして継続
/*
ここを埋めて完成させる
*/
}
dst[len] = '\0';
return len;
}
int main(void)
{
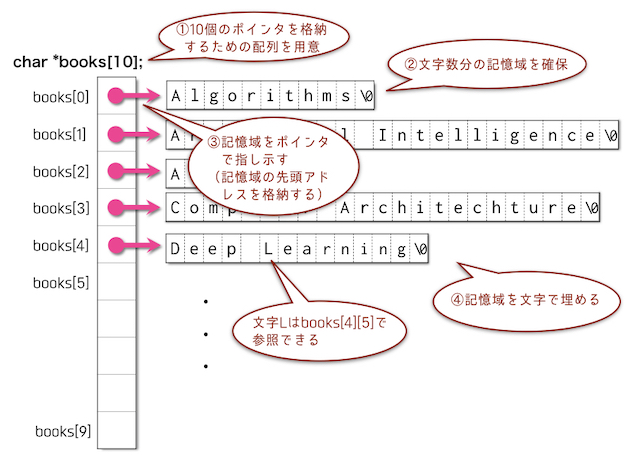
char *books[NUM]={NULL}; //各書名を示すNUM個のポインタからなる配列
char str[32]={0};
int i,j,len;
for(i=0; i<NUM; i++){
len = scrape(str,data[i]); //文字数と文字列の取り出し
[ 空欄ア ]; //書名を格納するための領域確保
if(books[i]==NULL){ //エラー処理
fprintf(stderr,"Error: Memory Allocation failure.\n");
for(j=0; j<i; j++) free(books[j]); //確保済領域の解放
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
for(j=0; j<=len; j++)
[ 空欄ウ ] = str[j]; //書名の格納(複数行可)
}
for(i=0; i<NUM; i++)
printf("%s\n",books[i]); //書名の表示
for(i=0; i<NUM; i++)
[ 空欄エ ] //NUM冊分の領域解法
return 0;
}